Bohnenberger, T., Jameson, A., Krüger, A., and Butz, A. Location-aware shopping assistance: Evaluation of a decision-theoretic approach. In Mobile HCI ’02: Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Mobile Human-Computer Interaction (London, UK, 2002), Springer-Verlag, pp. 155–169. [URL]
———
This paper describes a PDA-based system that give a shopper directions through a shopping mall on the basis of a) the types of products that the shopper has expressed an interest in; b) the shopper’s current location; c) the purchases that the shopper has made so far.
The authors built this system on the assumptions that the user might have a series of needs before going shopping. However, the authors cautions on how people often have considerable freedom in determining what particular location to visit for their shopping activities and that they might not have a clear understanding of their shopping needs.
One of the problem m-commerce application need to solve is how to deal with the uncertainties that are inherent to any attempt to match customers with products. For instance a user’s need might be generically specified as “something amusing to read on the plane”. These kind of needs might be difficult to operationalize for any intelligent interface.
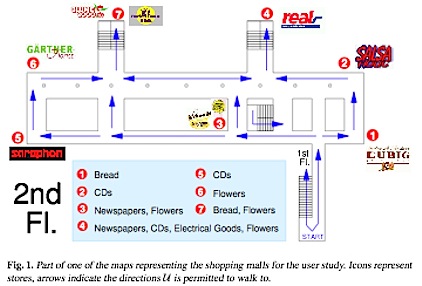
In the study reported in this paper the authors focused simply on optimizing the path the user has to take in order to buy a list of items. They built a PDA-based prototype and set up a fake shopping mall. They asked 10 user to shop with the PDA assistant and 10 with a paper map. They found that the group using the PDA solved the task faster.